Craig Charley
13 Feb 2014
Mammoth Guide to Webmaster Tools for SEO
Get hands on with Webmaster Tools on our brand new Advanced SEO Strategy Training course - the most up to date course on the market.
Google Webmaster Tools is an incredible tool for running health checks, monitoring your site's progress or uncovering the source of a problem. It's also an essential SEO tool.
If you're not familiar with Webmaster Tools or you haven't been keeping up with the latest changes & additions then we are here to help.
Learn about every feature of Google WMT and find out how you can use it for quick and long term SEO wins.

If you want to get hands on with Webmaster Tools then come down to Brighton for our 1-day SEO course which will give you hands on experience using WMT for SEO. We are always updating our SEO courses with the latest trends and best practices. If you're more interested in the analytics side of Webmaster Tools then we also recommend our 1 day Google Analytics or Advanced Google Analytics course.
I've thrown in a lot of tips along the way based on our experiences at Silicon Beach so you will have some good ideas to use Webmaster Tools to improve your site's performance.
Let's start from the top...
Site Dashboard
Messages
Check your messages. This is where Google will tell you if there is a serious problem with your site including technical issues and manual penalties.
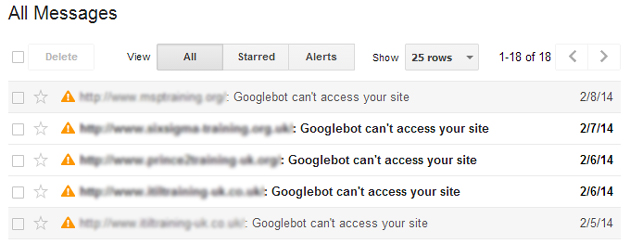
Essential Tip: Enable Email notifications by clicking Settings > Webmaster Tools Preferences. Tick ‘Enable email notifications’, choose ‘All issues’ and a preferred email address that is monitored daily. This way you are notified by any problems as soon as they happen and can act quickly.
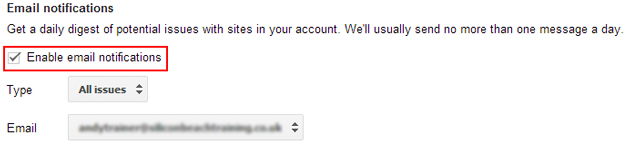
We recently had an issue where a group of sites we manage went down due to a server issue. We don't manage the sites on a regular basis so if it hadn't been for Email notifications then it could have been days before we noticed the problem! In that time Google could have decided to demote the sites and we would have lost any traffic.
Current Status
This is a snapshot of your site’s current status in the eyes of Google. You can quickly see site errors, search traffic and how many URLs are submitted – okay for a quick health check but not that informative without digging in deeper.
Search Appearance
Structured Data
Structured data is a markup languange used to give search engines a clearer picture of different elements on your site such as events, products, people etc.
Many of these elements are then reflected in search results with rich snippets like this:
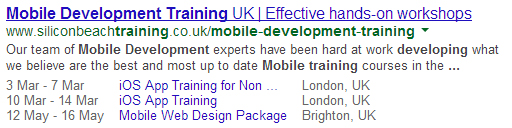
Structured data was one of the most important things to consider for webmasters in 2013 and in 2014 it is essential. Search engines are showing more and more information in SERPs and given them more data about your site can only help your visibility.
If you have added structured data to your site this section will tell you which elements Google has recognised and any issues with your mark-up.
Structured data is broken down into Data Types which should allow you to see if all your site's items are recognised.
If there are some items missing then you might have a problem with implementation.
If you have items with errors then you can click through to find the pages with issues.
To get started with Structured Data we recommend reading 'Getting started with schema.org'. We will also be covering it in more detail in a future post.
Data Highlighter
You may not have access to your site’s HTML or you might have a lengthy wait for development.
If this is the case then Data Highlighter is your best friend for adding structured data to your site without code.
We recommend always adding structured data directly onto your site so that it can be crawled by all search engines because the Data Highlighter is only recognised by Google but if you do want to use the tool then follow our simple tutorial to get started.
Data Highlighter allows you to highlight information on a page and give elements a ‘tag’.
This is a good way to test new structured data elements without making major changes to your site.
Don’t worry you don’t have to tag every page, the tool recognises elements on similar pages i.e. prices, dates, locations etc.
HTML Improvements
This section will give you a list of any technical improvements you can make to your site which may impact appearance in search.
Meta Descriptions do not have any algorithmic impact but can affect your CTR if not set up properly and if duplicate/missing/long/short then Google may decide to show its own description from on-page content.
Title Tags can affect your ranking and also CTR. Again, Google can choose to show its own title tags based on page content if not properly implemented but your title tags should also correspond to the page content. If spammy or irrelevant then you could be penalised or not visible for related searches.
Non-indexable Content is pages that Google cannot index due to HTML problems and should be fixed as soon as possible.
Sitelinks
Sitelinks usually show up for branded searches and sometimes for searches where Google decides one result is the most important. They are automatically generated by Google and link to the most relevant and/or popular pages related to the search.
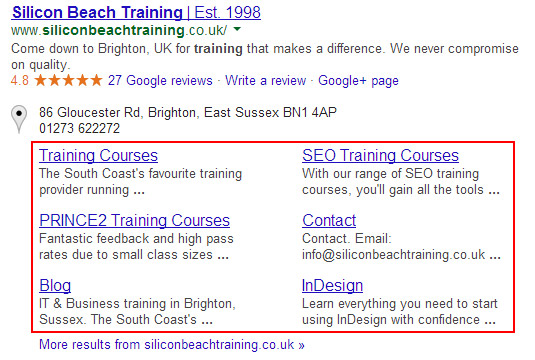
Sometimes you might disagree with Google’s choice of sitelinks and can use this section to demote a URL to stop it showing as a sitelink. Simply enter the unwanted URL and click 'demote', it can take some time for changes to be reflected in SERPs.
Search Traffic
Search Queries
Top Queries is nowhere near as useful (or accurate) as Google Analytics and so should be treated with care, but it does give a snapshot of recent search performance and the filters can be used to get some more interesting data.
Since Google withdrew organic data from Google Analytics (due to SSL search), this section is now the only ‘official’ place to find out which queries are sending the most traffic to your site.
Because this section shows impressions data it is a good way to check the performance of your ranking pages.
If a keyword has a lot of impressions and a good average position but a low CTR then you might need to do improve your meta title and meta description to encourage more clicks.
Although Top Queries now provides more detail (impressions & clicks used to be rounded) and so looks accurate, the numbers differ quite a look to Analytics so this data should not be used in isol
Top Pages gives you a snapshot of the most popular pages in Google search. Again, this section is useful for improving CTR.
You can find some hidden opportunities in this section by filtering results 10+ impressions/clicks and then sorting by CTR low to high.
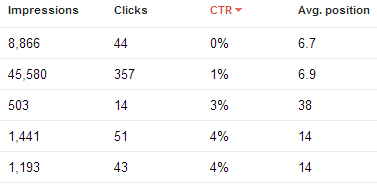
These pages are appearing for high value keywords but are not attracting clicks. Usually this is because you rank near the bottom on the SERP or the result itself does not attract clicks.
- If your average postition is bad then you might be able to do some work on the page with the knowledge that the rewards will be great.
- If your average position is good then work on improving your meta title and description or gaining rich snippets to make your result stand out and attract clicks.
Links to Your Site
This section can be misleading; it does not list all the links to your site and a huge number of the links listed will no longer exist.
It is also very unlikely that this is how Google sees your backlink profile. In Webmaster Tools help they describe the section as a 'sampling' and say:
"Not all links to your site may be listed. This is normal."
Tools like Majestic SEO Open Site Explorer give a much more accurate representation of the active links to your site.
Google will certainly have a more accurate index but they choose not to share it with all webmasters.
However, this section is useful for cleaning up links and easily finding any sites that are sending a lot of links your way - manual notifications often include references to links straight from the Links to your Site section.
Generally we recommend using 3rd party tools like Majestic or LinkRisk for link removal campaigns as it will save you time checking pages that are no longer linking to your site. If you do use Google's data then at least use a tool to crawl the links to make sure you're not wasting time checking 404 pages.
The anchor text section also gives you an idea of the keywords that Google associates with your site.
Internal Links
Your Internal Links list can be used to find any links to pages that you're planning on removing to avoid broken links on your site.
It also gives you an idea of how Google sees your site. Put simply, the most linked to pages are the ones that Google will see as your most important:
The number of internal links pointing to a page is a signal to search engines about the relative importance of that page. If an important page does not appear in this list, or if a less important page has a relatively large number of internal links, you should consider reviewing your internal link structure.
Manual Actions
A notification will appear here if a member of the Google Webmaster Spam team has decided that you have done something against the Webmaster Guidelines. There are two types of action:
- Site-wide matches - your entire site has been demoted
- Partial matches – a page or section on your site has been demoted
Manual penalties can be hard to undo but this section is a good place to start if traffic has plummeted.
Hopefully this section will be empty! If not, here is a guide to the messages and how to start the reconsideration process:
| Manual Action | Issue | Action Required |
|---|---|---|
| Unnatural links to your site – impacts links | Google has detected unnatural links to your site and has taken action against those links, not your site. | Your site might lose ranking due to lost links but there is no action against your site to undo. Work on building better links. |
| Unnatural links to your siteUnnatural links to your site | Google has detected unnatural links to your site and has applied a manual spam action. Your site or sections of your site will no longer rank. |
Run a link removal campaign to remove as many bad links as possible, use the disavow tool to disavow any remaining links, submit a reconsideration request to Google including documentation of your link removal campaign. Ranking might not recover even after successful reconsideration as link value has been diminished. |
| Unnatural links from your site | Google has detected unnatural links on your site. Your site or sections of your site will no longer rank. | Review your outbound links and remove or nofollow any that violate Google’s Webmaster Guidelines. Submit a reconsideration request once complete. |
| Hacked site | Your site appears to have been hacked by a third party. Google will reduce the visibility of your site and add a warning label in SERPs. |
Assess the damage, clean the site, request a review. For more info see Google's Hacked Help Page |
| Thin content with little or no added value | Google has detected low quality pages on your site. These pages or your whole site will no longer rank. | Run a content audit to establish weak pages. Find and remove duplicate content. Improve or delete weak pages ensuring that your site provides unique, informative content. Submit a reconsideration request. |
| Pure spam | Google has detected that your site or pages on your site are using techniques that violate the Webmaster Guidelines such as cloaking, scraping, auto-generated gibberish. Your site or sections of your site will no longer rank. | Run a site audit to identify problem areas and clean the site to meet the Webmaster Guidelines. Submit a reconsideration request. |
| User-generated spam | Google has detected user-generated spam on your site – usually forum posts, blog comments, guestbook entries, user profiles. Your site or sections of your site will no longer rank. | Identify and remove all user-generated spam. Consider implementing measures to prevent user-generated spam such as moderation and spam filters. Submit a reconsideration request. |
| Cloaking and/or sneaky redirects | Google has detected that you are showing different content to users than to robots using cloaking or redirected. Your site or sections of your site will no longer rank. | Use Fetch as Google to compare content seen by robots to content seen by humans. Clean up any pages where different content is shown or different redirects occur. Once happy that the site is clean, submit a reconsideration request. |
| Hidden text and/or keyword stuffing | Google has detected that you’re either trying very outdated SEO techniques or have forgotten to clean up old pages. Your site or sections of your site will no longer rank. | Clean up offending pages. Use View Page Source to find hidden content, select all on the page to find text that is the same colour as the background, remove keyword stuffing or reduce number of keywords on a page. Submit a reconsideration request. |
| Spammy freehosts | Only relevant if you host other sites or services. If a significant number of sites or services on one host are spammy then Google will take action against the service as a whole. | Remove existing spammy accounts. Take steps to establish a quality barrier for your service. Submit a reconsideration request. |
| Image mismatch | Google has detected that your site is displaying different images to their search results. These images will no longer show in search results. | Make sure that images are showing the same on your site and in search results, any issues might be a result of anti-hotlinking. Once you are satisfied that the same results are showing, submit a reconsideration request. |
Google Index
Index Status
Basic shows the number of URLS that Google has in its index in the past 12 months.
Advanced also shows URLS ever crawls, URLS blocked by robots and URLS removed from the index.
This section is useful for checking indexing issues.
If there are more URLs than expected then you might want to consider noindexing category or tag pages and might have a duplicate content issue.
If there are fewer URLs than expected then you might be blocking sections of your site with robots.txt or noindex/nofollow tags.
Content Keywords
If you want to find out what words and phrases Google associates with your site then Content Keywords gives you a good idea.
It is a list of the most common words and phrases (with variants) across all pages of your site (minus common words).
Use this section to check for anomalies – is there a topic that isn’t relevant? Is there an important topic missing? Use your content strategy to affect the list.
Remove URLs
Ideally you should use robots.txt or nofollow, noindex tags to stop Google from indexing specific URLs on your site. However, if you want a page removed more quickly or are waiting in a queue for the dev team then you can use this tool to quickly remove URLs.
To use the tool enter the URL you want removed and choose Remove page from search results and cache, Remove page from cache only or Remove directory depending on your desired outcome.
The most useful action is remove page from cache only which is ideal when you have updated a page on your site but Google is taking a long time to update the cached version in results.
Crawl
Crawl Errors
Site Errors can have a dramatic effect on your visibility in search engines so you want three green ticks at all times.
If there are problems with any of the above then you might have a major issue with your website which needs fixing both for users and for Google to rank your site.
URL Errors will give you a list of pages that Google has previously indexed (or found links to) that are returning an error. These are divided into Server error and Not found.
Server errors are returned when your server is taking too long to respond (often caused by crawler overload) or your site is down.
Not found results are usually 404s. Either you have deleted a page and not redirected the URL, or somebody has incorrectly linked to your site. It is recommended to regularly monitor not found results to make sure than any important pages are redirected. Clicking on a URL brings up a list of sites linking so you can make sure you’re not losing any quality link value.
URL errors are also split by Google’s three crawlers – Web, Smartphone and Feature Phone. It is useful to check all three, especially if you have a separate mobile site or dynamic content.
Crawl Stats
Find out how Google crawls your site with Crawl Stats including pages crawled per day, kilobytes downloaded per day and time spent downloading a page.
Each graph gives a snapshot of how Google is crawling your site and any changes to frequency and speed. It is useful to gauge average page speed (you want it low) and how often Google crawls your site. If the crawl rate seems unnecessarily large and is overloading your servers you might want to look into reducing it.
Fetch as Google
‘Fetch as Google’ allows you to force Google to crawl a URL and can be very useful for finding errors and for quicker indexing.
Enter your URL into the form, choose your crawler and click fetch.
If successful you will see a tick and ‘Success’, if unsuccessful a warning and ‘Not found’:
This is useful firstly as a quick way to see if Google can access a page – and see what content is returned by clicking on the ‘Success’ link. You can also test web and mobile crawlers if you have different mobile content to check that your site is properly set up.
Fetch as Google also allows you to submit the crawled URL (and linked pages) to be indexed. This is ideal if your site is not set up to ping Google when you publish a new page or update content.
Blocked URLS
Block URLs tells you how many pages Google has tried to crawl in the past 90 days but has been prevented by robots.txt. There are no links to the URLs (you can get this information from the Crawl Errors tab!) so you might think this page is redundant, but it actually contains a nice little tool for testing your robots.txt file!
In the first box you can see your current robots.txt, in the second box you can enter URLs to test against.
You can use this tool to check if robots.txt is doing what you want it to (by testing against URLs you want to be crawled and that you want blocked) and also to test robots.txt changes without affecting your live website.
Sitemaps
Use the Sitemaps tab to make sure that Google has processed your sitemap(s), check for errors and compare the number of pages submitted to the number of pages indexed.
If there is a large difference then you might have an issue. You might be blocking some of the pages in your sitemap with robots.txt or some pages might be violating Google’s Webmaster Guidelines.
This is also the place to submit your most up to date sitemap rather than waiting for Google to recrawl your site (similar to the Fetch as Google tool but for sitemaps!).
URL Parameters
Avoid unnecessary crawling and duplicate content issues with URL Parameters. Using this tool can have serious consequences if used incorrectly so be carefully adding any Parameters.
If you have multiple URLs pointing at one piece of content – due to sorting, session ID, filters etc. – then it can be good to give Google an indication which URL is the ‘best’ one.
We recommend only using this tool if you have crawl issues (your site is going down or not being crawled quickly enough). Instead you can use rel=canonical tags in the
of a page to specify the correct URL to Google; this way Google still crawls all of your content but knows which URL to index.
Security Issues
If Google detects that your site has been compromised then it will detail the problem in this section.
It is important to fix any security issues as soon as possible. Not only are they bad for your visitors, but they can hurt ranking. Best scenario, Google adds a ‘This site may harm your computer’ tag to the search result. Worst scenario, your entire site is dropped from results.
As mentioned earlier in the advice for hacked sites, we recommend contacting your web team or visiting Google’s hacked sites resource for help.
Other Resources
Simply lists links to other Google products and tools (some already contained in Webmaster Tools).
The most important for analysing your site is PageSpeed Insights but we will cover that in a future post.
Labs
Labs included Authorship and Instant Preview but as of July 2014 no longer exists.
To Sum Up
If you are responsible for a website then it is essential to know and treat Webmaster Tools like your best friend.
It is one of the best ways to pick up easy wins, missed opportunities and critical mistakes.
Have we missed any other ways you can use Webmaster Tools to improve SEO? Let us know by commenting below.
