Andy Trainer
4 Jul 2013
PRINCE2 Process Diagrams
We decided that PRINCE2® diagrams could do with a freshen up so we've created an easy to read, standardised set of diagrams covering the 7 PRINCE2 processes to help learn PRINCE2.
Starting with the PRINCE2 Process Model and then breaking it down into each of the 7 processes.
If you've ever searched Google for 'PRINCE2 diagrams' you will know that it's not a pretty sight, and a lot of those diagrams are either too plain or impossible to decipher.
Our set of diagrams makes the PRINCE2 processes easier to understand by complimenting your PRINCE2 pre-course work and manual when preparing for your PRINCE2 Practitioner Exam.
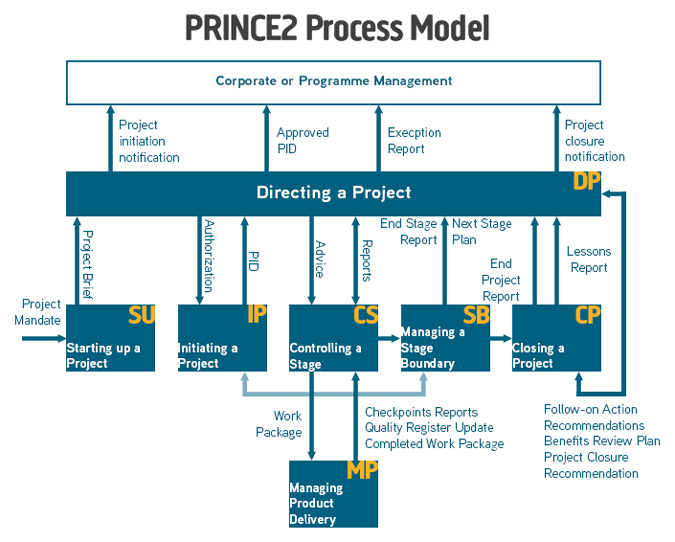
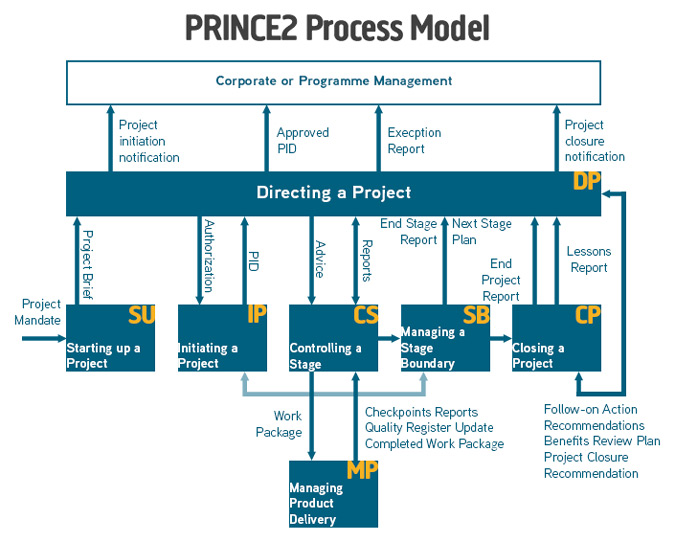
PRINCE2 Process Model
PRINCE2 describes the steps of project management in seven processes. Any PRINCE2 project will need to address each of the processes but the extent of the application of a process should be decided on a project by project basis.
The PRINCE2 Process Model below describes the relationship between the seven processes:
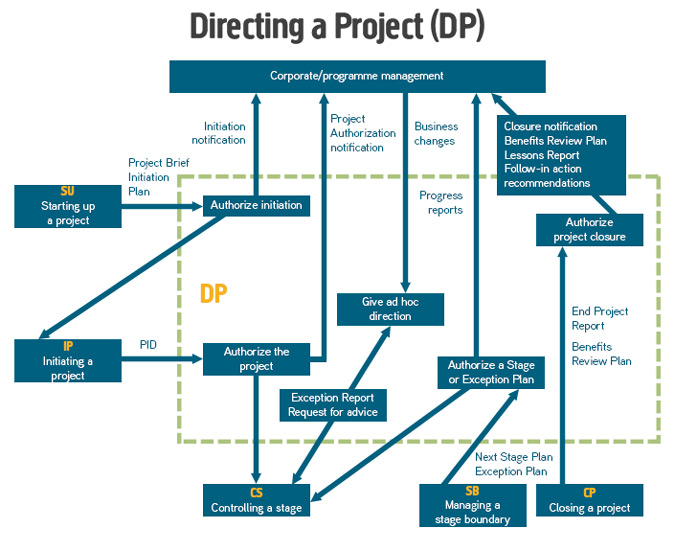
Directing a Project (DP)
Directing a Project covers the decision-making process of running a project and is aimed at the Project Board, the management team representing the sponsor, the users of the final product and the suppliers of the product. This process ensures that these people are only involved in the most important decisions of the project and not the day to day management.
More reading:
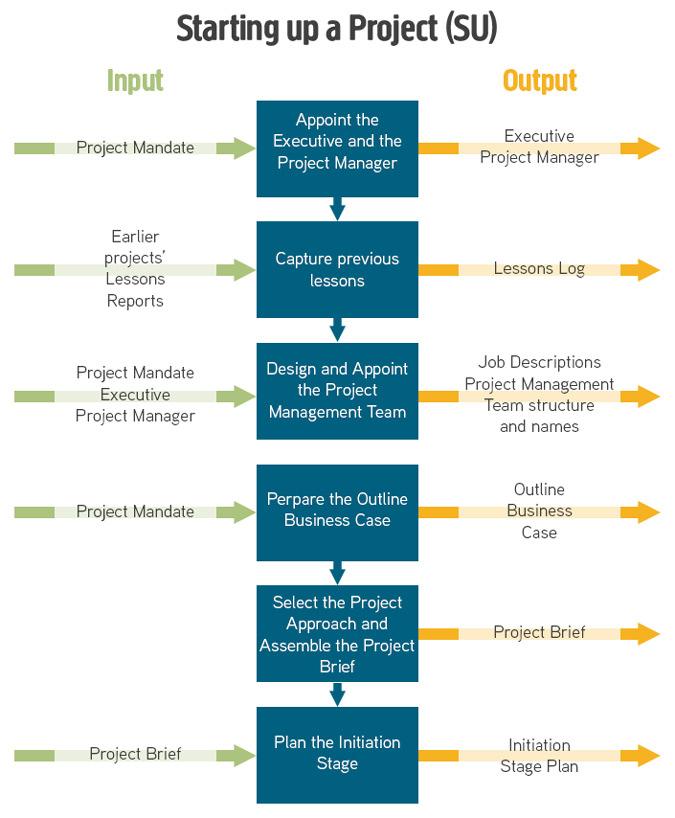
Starting up a Project (SU)
This is a short but very important pre-project process to gather basic information about the project. Starting up a Project includes six steps:
- Appoint the Executive and the Project Manager
- Capture previous lessons
- Design and Appoint the Project Management Team
- Prepare the Outline Business Case
- Select the Project Approach and Assemble the Project Brief
- Plan the Initiation Stage
More reading:
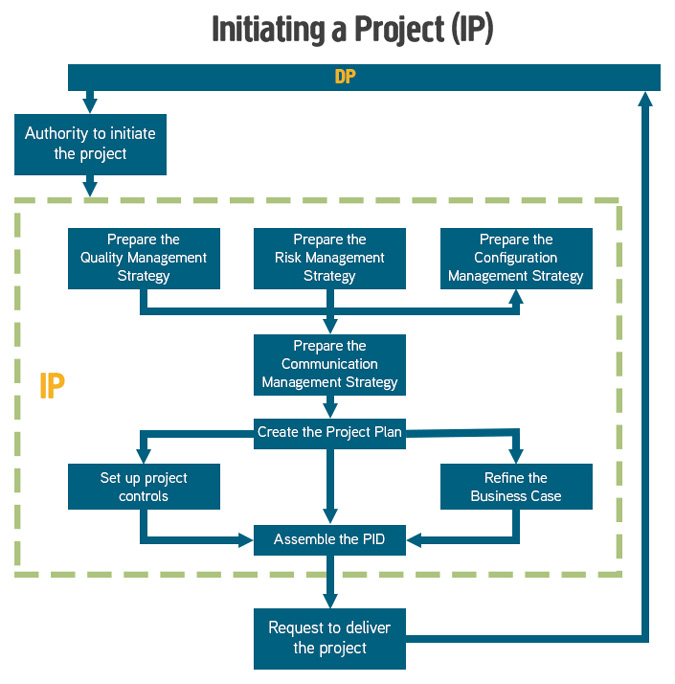
Initiating a Project (IP)
Initiating a Project ensures that all stakeholders have reached an agreement before significant spend. Agreements should be reached on what is to be done; how, when and why it is being done; the expected benefits and how the required quality will be achieved.
More reading:
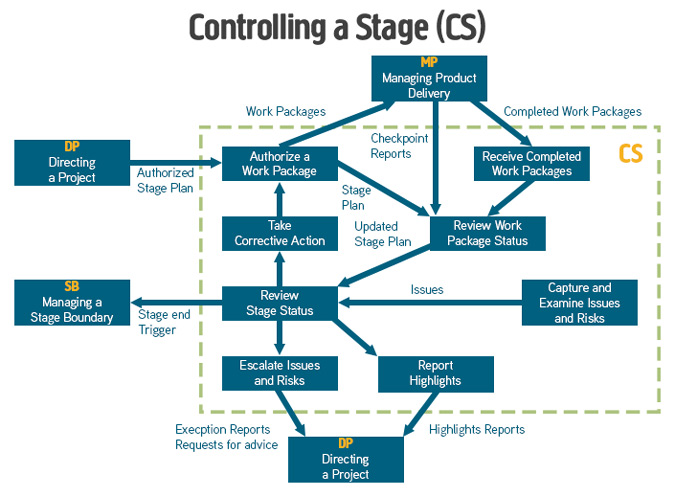
Controlling a Stage (CS)
This process describes the core activities of the Project Manager and ensures that a stage stays within budget and schedule and to the customers' required quality.
More reading:
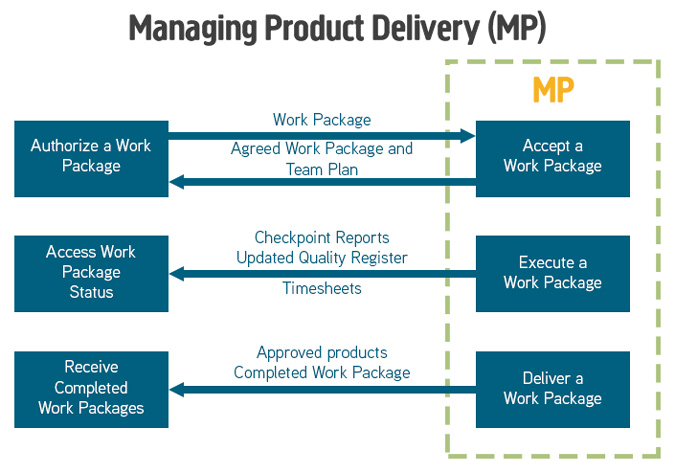
Managing Product Delivery (MP)
This process describes the link between the Project Manager and Team Manager(s) and is especially important when teams are external and not using PRINCE2. The work agreed includes times and dates, quality, and reporting.
More reading:
PRINCE2 - Managing Product Delivery
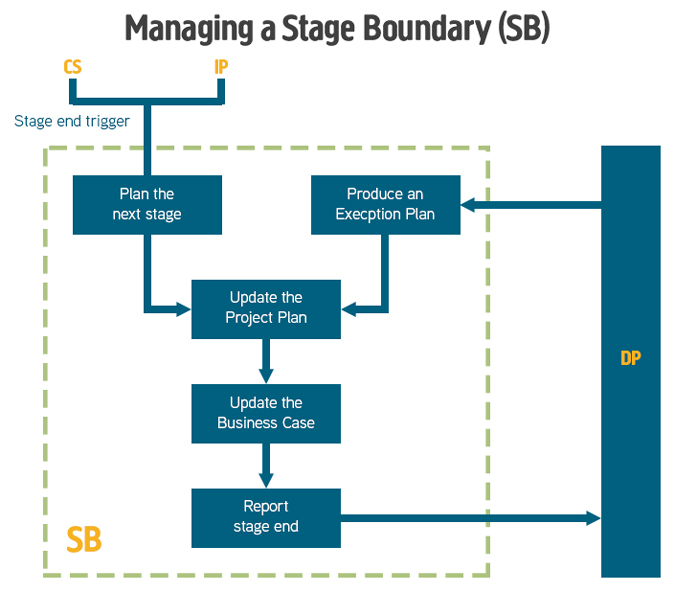
Managing a Stage Boundary (SB)
This process checks the work from the current stages and plans the next stage. The Project Plan and Business Case are updated and the outcome of the stage which has ended is reported by the Project Manager to the Project Board who then approve moving into the next stage.
More reading:
PRINCE2 - Managing a Stage Boundary
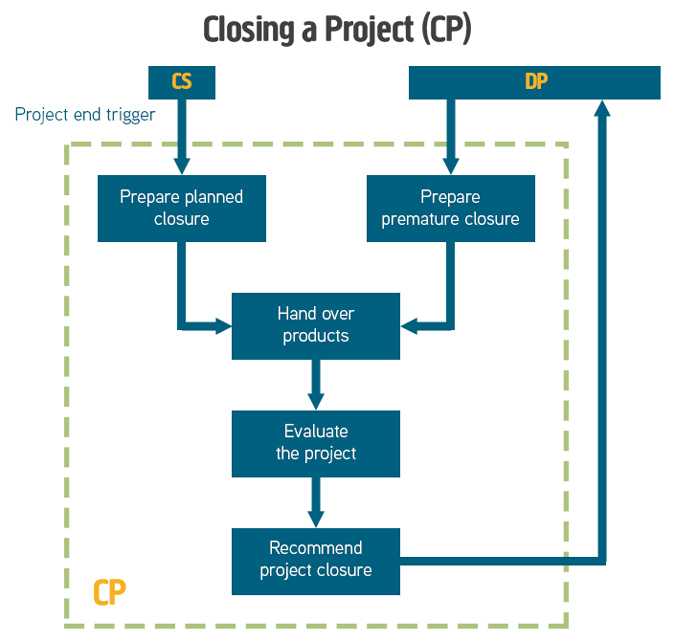
Closing a Project (CP)
The Closing a Project process occurs either at a project's natural end or when premature closure is required. Closure of the Project confirms the acceptance of the project product and that the objectives set out in the Project Initiation Document have been achieved.
More reading:
PRINCE2® is a registered trade mark of AXELOS Limited.